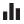
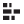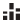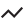Which chart is right for you? That depends on the data and purpose of your chart.
| IF i want a... | of data like… | i should use A... |
|---|---|---|
|
Comparison |
total revenue per month |
|
|
revenue per month, per product |
|
|
|
Trend |
product sales by region; volume of stock trading vs. close price |
|
|
revenue by project type; project cost and project hours |
|
|
|
contribution per product to profit over time |
|
|
|
Ratio |
% each salesperson contributes to total sales |
|
|
progress through a process, like a sales pipeline |
|
|
|
Relationship |
project cost vs. return on investment (ROI) |
|
|
prospective sales by estimated close date, $ amount, and probability of close |
|
|
|
Performance |
performance against a goal I set; total number of units sold |
|
For more details, see Select a Chart Type.